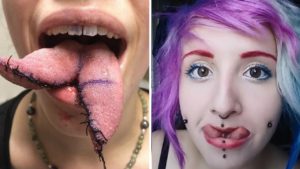
Tongue Splitting, Nipple Excision, And Ear Removal: Why Prosecute The Operator But Not The Customer?
By Charles Foster
Image: ‘Split tongue: procedure, safety, result’: Tattoo World: Standard YouTube licence.
The appellant in R v BM was a tattooist and body piercer who also engaged in ‘body modification’. He was charged with three offences of wounding with intent to do grievous bodily harm. These entailed: (a) Removal of an ear; (b) Removal of a nipple; and (c) division of a tongue so that it looked reptilian. In each case the customer had consented. There was, said the appellant, no offence because of this consent.
Where an adult decides to do something that is not prohibited by the law, the law will generally not interfere.
In Schloendorff v Society of New York Hospital (1914) 105 NE 92 Cardozo J said:
“Every human being of adult years and sound mind has a right to determine what shall be done with his own body.”[1]
This principle has been fairly consistently recognised in the English law.[2] Thus, for instance, In In re T (Adult: Refusal of Treatment, Butler-Sloss LJ cited with approval this section of the judgment of Robins JA in Malette v Shulman[3]:
‘The right to determine what shall be done with one’s own body is a fundamental right in our society. The concepts inherent in this right are the bedrock upon which the principles of self-determination and individual autonomy are based. Free individual choice in matters affecting this right should, in my opinion, be accorded very high priority.’Read More »Tongue Splitting, Nipple Excision, And Ear Removal: Why Prosecute The Operator But Not The Customer?