Lifesaving Treatment for Babies Born at 22 weeks Doesn’t Mean Abortion Law Should Change.
Kristina Bessolova/Shutterstock
Dominic Wilkinson, University of Oxford
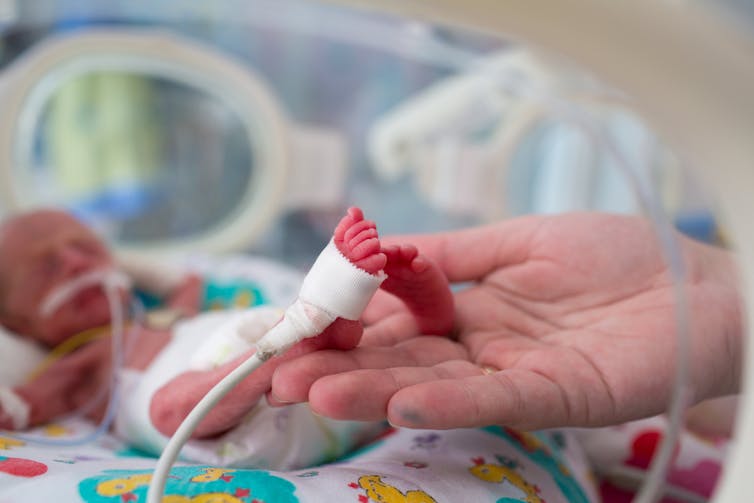
When new guidance relating to the outcome and medical care of babies born extremely prematurely was recently released, it led some to call for UK abortion law to be revised.
This was because one of the new recommendations from the British Association of Perinatal Medicine is that it is sometimes appropriate to provide resuscitation and active medical treatment for babies born at 22 weeks gestation (four and a half months before their due date). This is a week earlier than was recommended in the last version of the framework, published in 2008.
The argument goes that the new guidance creates a “contradiction in British law” because extremely premature infants can now be resuscitated before the point in pregnancy where abortion law changes.
A spokesperson for campaign group Right to Life UK said: “In one room of a hospital, doctors could be working to save a baby born alive before 24 weeks whilst in another room a doctor could perform an abortion which would end the life of a baby at the same age. Surely this contradiction needs to end?”Read More »Lifesaving Treatment for Babies Born at 22 weeks Doesn’t Mean Abortion Law Should Change.


