How Does Social Media Pose a Threat to Autonomy?
Undergraduate Finalist paper in the 2025 National Uehiro Oxford Essay Prize in Practical Ethics. By Rahul Lakhanpaul, University of Edinburgh.
Undergraduate Finalist paper in the 2025 National Uehiro Oxford Essay Prize in Practical Ethics. By Rahul Lakhanpaul, University of Edinburgh.
Written by Eliora Henzler, MSt in Practical Ethics, University of Oxford EXTRATERRITORIAL MIGRATION MANAGEMENT How can states ethically justify deporting individuals to third countries? In October 2024, a ship of the Italian coast guard disembarked in the port of Shëngjin, in Albania. After a few days, it began a voyage in the opposite direction. Italy… Read More »What are the Ethics of Sending a Person to a Country They are not From?
Written by Rebecca Brown There has been plenty of debate about women’s right to choose how they give birth. Some of it stems from the negative experiences of women who have felt unable to have the birth they want, instead being pressured or even coerced into delivering their child according to health professionals’ preferences. At… Read More »Trampolining Whilst Pregnant And Women’s Autonomy
Written by Rebecca Brown Imagine going to a cafe for a drink and snack. At some point you need the loo – you go to the bathroom but discover the toilet seat is higher than your waist! Somehow you manage to clamber up, unfortunately touching parts of a toilet you would prefer you didn’t have… Read More »Building A World People Can Use
Written by Joseph Moore Earlier this year, Alex Ruck Keene KC (Hon) delivered a Practical Ethics and Law Lecture at the Uehiro Centre on the topic of consent and autonomy-based arguments in medical ethics and law, to which the Centre’s Esther Braun responded. In the course of this enlightening discussion (and in private conversation since),… Read More »Consenting to or Requesting Medical Care?
This article received an honourable mention in the graduate category of the 2024 National Oxford Uehiro Prize in Practical Ethics. Written by Beatrice Marchegiani. Introduction Recent advancements in Large Language Models have enabled AI systems to engage in conversations with users that are virtually indistinguishable from human interactions. The proliferation of advanced Conversational AIs (CAIs)1… Read More »National Oxford Uehiro Prize in Practical Ethics: Undisclosed Conversational AIs: A Threat to Users’ Autonomy
Written by Rebecca Brown.
This is the fourth in a series of blogposts by the members of the Expanding Autonomy project, funded by the Arts and Humanities Research Council.
This blog is based on a paper forthcoming in Episteme. The full text is available here.
Imagine you are sick with severe headaches, dizziness and a nasty cough. You go to see a doctor. She tells you you have a disease called maladitis and it is treatable with a drug called anti-mal. If you take anti-mal every day for a week the symptoms of maladitis should resolve completely. If you don’t treat the maladitis, you will continue to experience your symptoms for a number of weeks, though it should resolve eventually. In a small number of cases, maladitis can become chronic. She also tells you about some side-effects of anti-mal: it can cause nausea, fatigue and an itchy rash. But since these are generally mild and temporary, your doctor suggests that they are worth risking in order to treat your maladitis. You have no medical training and have never heard of maladitis or anti-mal before. What should you do?
One option is that you a) form the belief that you have maladitis and b) take the anti-mal to treat it. Your doctor, after all, has relevant training and expertise in this area, and she believes that you have maladitis and should take anti-mal.Read More »Expertise and Autonomy in Medical Decision Making
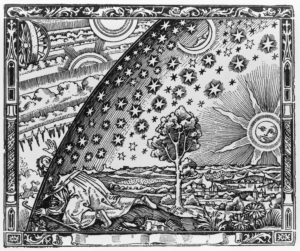
Provided my eyes are not withdrawn from that spectacle, of which they never tire; provided I may look upon the sun and the moon and gaze at the other planets; provided I may trace their risings and settings, their periods and the causes of their travelling faster or slower; provided I may behold all the stars that shine at night – some fixed, others not travelling far afield but circling within the same area; some suddenly shooting forth, and others dazzling the eye with scattered fire, as if they are falling, or gliding past with a long trail of blazing light; provided I can commune with these and, so far as humans may, associate with the divine, and provided I can keep my mind always directed upwards, striving for a vision of kindred things – what does it matter what ground I stand on?
Seneca, Consolation to Helvia, translated by C. D. N. Costa
Read More »Stoicism as a Foundational Component of Ethics and Existentialism
Written by Sarah Raskoff
(Post is based on my recently published paper in Bioethics)
Nudges are small changes in the presentation of options that make a predictable impact on people’s decisions. Proponents of nudges often claim that they are justified as paternalistic interventions that respect autonomy: they lead people to make better choices, while still allowing them to choose for themselves. A classic example is changing the location of food items in a cafeteria so that healthier choices are more salient. The salience of healthy foods predictably leads people to select them, even though they are still free to select the unhealthy options, too.
Nudges have become increasingly popular, but there are many objections to their widespread use. Some allege that nudges do not actually benefit people, while others suspect that they do not really respect autonomy. Although there are many ways of making sense of this latter concern, in a recent paper, I develop a new version of this objection, which takes as its starting point the observation that people often have incomplete preferences.Read More »Nudges and Incomplete Preferences
Laws on genital mutilation, gender affirmation and cosmetic genital surgery are at odds. The key criteria should be medical necessity and consent.
By Brian D. Earp (@briandavidearp)
———————-
In Ohio, USA, lawmakers are currently considering the Save Adolescents from Experimentation (SAFE) Act that would ban hormones or surgeries for minors who identify as transgender or non-binary. In April this year, Alabama passed similar legislation.
Alleging anti-trans prejudice, opponents of such legislation say these bans will stop trans youth from accessing necessary healthcare, citing guidance from the American Psychiatric Association, the American Medical Association and the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Providers of gender-affirming services point out that puberty-suppressing medications and hormone therapies are considered standard-of-care for trans adolescents who qualify. Neither is administered before puberty, with younger children receiving psychosocial support only. Meanwhile genital surgeries for gender affirmation are rarely performed before age 18.
Nevertheless, proponents of the new laws say they are needed to protect vulnerable minors from understudied medical risks and potentially lifelong bodily harms. Proponents note that irreversible mastectomies are increasingly performed before the age of legal majority.
Republican legislators in several states argue that if a child’s breasts or genitalia are ‘healthy’, there is no medical or ethical justification to use hormones or surgeries to alter those parts of the body.
However, while trans adolescents struggle to access voluntary services and rarely undergo genital surgeries prior to adulthood, non-trans-identifying children in the United States and elsewhere are routinely subjected to medically unnecessary surgeries affecting their healthy sexual anatomy — without opposition from conservative lawmakers.