Written by César Palacios-González
It has been recently reported (link in Spanish) that a 32 year old Greek woman is 27 weeks pregnant with a child who was conceived after a mitochondrial replacement technique (MRT) – in this case Maternal Spindle Transfer (MST). If true this is really big news in terms of reproductive medicine and biotechnology, we are still waiting for data to be published. If successful, this would be just the third birth following a reproductive technique that mixes the DNA of three people (you will probably remember the big media buzz a couple of years ago about ‘three parent babies’). This newest feat was achieved by a group of Spanish and Greek scientists; the clinical trial was carried out in Greece due to the fact that in Spain MRTs are not on the list of authorised reproductive techniques.
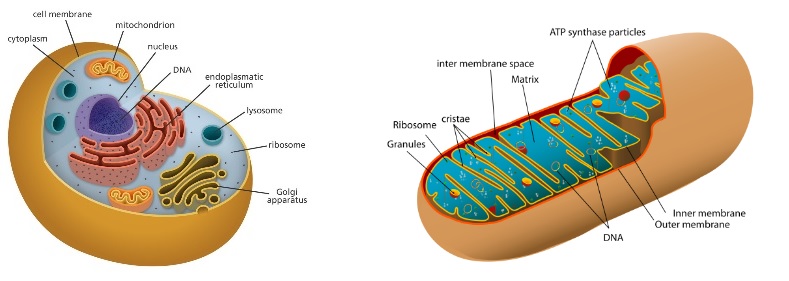
Before discussing what I consider to be the main ethical issue with this case, let us talk a bit about mitochondria and MRTs. Every human egg contains thousands upon thousands of mitochondrion. These tiny organelles have the really important task of producing the energy (in the form of ATP) that first the egg, then the developing embryo, and finally the human adult need to adequately function. It is thus not strange that when mitochondria do not work as they should the human body ‘malfunctions’. And it is also not strange that mitochondrial dysfunction more significantly affects the organs that require the most energy, for example the brain and the muscles.
To understand, broadly, what can go wrong with mitochondria, we need to bear in mind two of their characteristics: a) that they have their own DNA, and b) that they are mostly solely maternally transmitted. Regarding the former, inside every nucleated human cell there is nuclear DNA (nDNA) and there is mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
Read More »A third MRT-baby is on its way